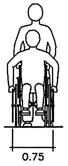Законодательство
V. Appendices
1. Wheelchair users |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Overcoming differences in level between road and pavement | • Install curb ramps | ||||||||||||
| • Bridging great differences in height usually tackled by providing stairs | • Provide ramps, wide elevator cabs or platform lifts | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in tight spaces | • Provide wide routes and spaces | ||||||||||||
| • Passing through narrow door openings and over high thresholds | • Provide sufficiently wide door openings with low beveled thresholds or none at all | ||||||||||||
| • Reaching high-mounted controls and objects | • Provide low-mounted controls | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in rest rooms | • Install grab bars, bath-tub and shower seats | ||||||||||||
2. People with limited walking abilities |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Overcoming differences in level | • Provide curb ramps, ramps, elevators or platform lifts | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in situations requiring speed | • Increase the pedestrian crossing time interval • Increase the opening interval of elevators and automatic doors |
||||||||||||
| • Climbing stairs and ramps | • Provide handrails for gripping | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in rest rooms | • Provide sufficiently wide rest rooms • Provide grab bars, bath-tub and a shower seat |
||||||||||||
| • Passing through narrow door openings and over high thresholds | • Provide sufficiently wide door openings with low beveled thresholds or none at all | ||||||||||||
3. People with limited use of hands or arms |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Opening heavy doors | • Use automatic or easy-to-open doors | ||||||||||||
| • Gripping door knobs | • Use lever-type door handles | ||||||||||||
| • Gripping faucets | • Use lever-type or push-buttons faucets | ||||||||||||
4. The sightless |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Orientation | • Provide guide strips within the pathway surface • Provide raised curbs and other detectable guiding elements • Provide tactile marking strips to indicate changes in direction and the location of stairs and ramps |
||||||||||||
| • Identifying obstructions within the path of travel | • Provide textured paving or tactile marking strips around obstructions | ||||||||||||
| • Crossing roads | • Provide audible traffic signals | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in elevators | • Provide audible signals and call buttons with tactile text | ||||||||||||
| • Recognizing emergency situations | • Provide audible alarm signals | ||||||||||||
| • Locating exit doors and stairs | • Provide tactile marking around the knobs of exit doors and the handrails of exit | ||||||||||||
5. The partially sighted |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Identifying obstructions within the path of travel | • Provide bright-coloured markings or signals to identify obstructions | ||||||||||||
| • Orientation | • Provide clearly legible lettering and sufficiently large dimensions for direction signs | ||||||||||||
| • Crossing roads | • Provide audible traffic signals | ||||||||||||
| • Maneuvering in elevators and in emergency situations | • Use contrasting colour for doors, handrails, tactile signs, etc | ||||||||||||
| • Locating facilities | • Provide alarm signals | ||||||||||||
6. The hearing impaired |
|||||||||||||
| Problem
|
Measure
|
||||||||||||
| • Crossing roads | • Provide clearly visible coloured signs and traffic signals | ||||||||||||
| • Managing in situations involving the use of speech messages, verbal transmission and interaction | • Use clearly written messages, especially in emergency situations Install induction loops in assembly halls and in public telephones | ||||||||||||
| • Not hearing door, elevator and emergency | • Provide flashing light signals | ||||||||||||
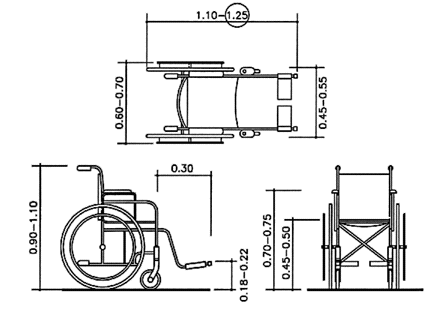
Dimensional data varies from one person to another, and the average dimensions vary from one country to another. The dimensions of the individual human being vary with time. The tables below provide a range of dimensions derived from various studies (see Comparative Tables). The given measurements take into consideration size variation between males and females as well as between different persons of the same sex. Wheelchair Dimensions (fig.1) Dimensions shown in the figure are of a conventional manual wheelchair. The larger, encircled dimensions refer to electric wheelchairs. |
|||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
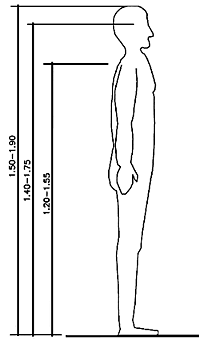
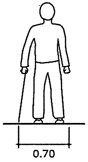
Dimensional data to a normal person (fig. 2)
|
|
||||||||||||
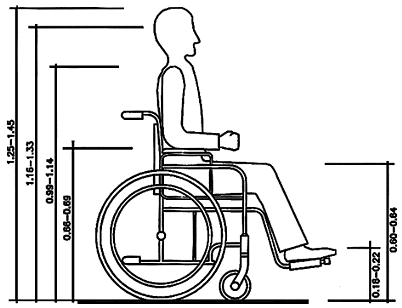
Dimensional data of a wheelchair user
|
|||||||||||||
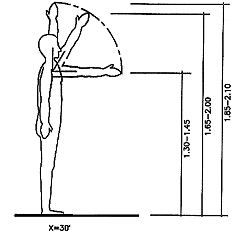
Reaching zones of a normal person (fig. 4)
|
|
||||||||||||
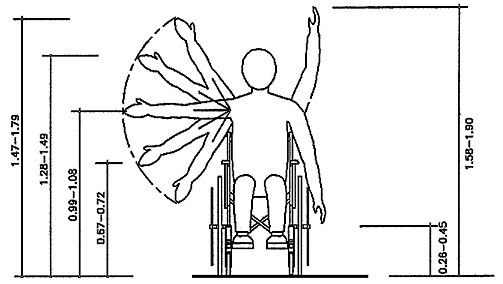
Vertical reaching zones of a wheelchair user
|
|||||||||||||
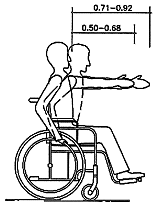
Horizontal forward reach of a wheelchair user (fig. 6)
|
|
||||||||||||
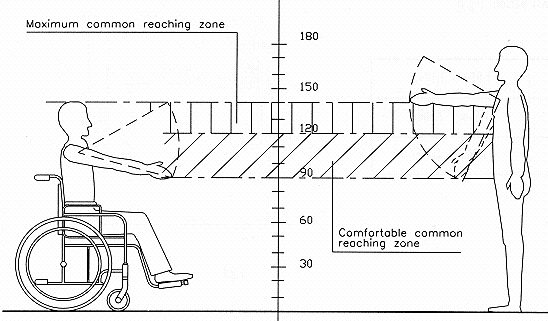
Common reaching zone
|
|||||||||||||
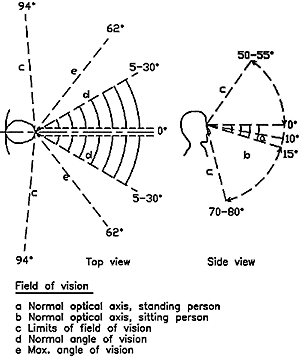
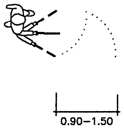
Field of Vision
|
|||||||||||||
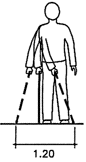
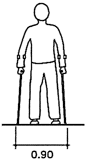
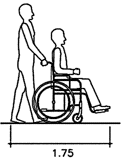
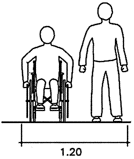
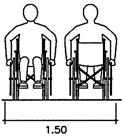
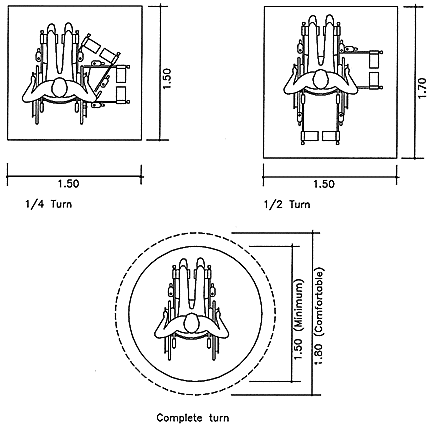
Pathway dimensions
Fig. 9 Wheelchair maneuvering space
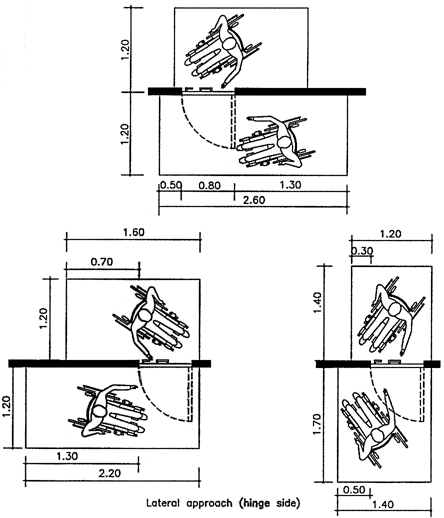
Maneuvering at doors
|
|||||||||||||
| Назад | Оглавление | Далее |